Overview
Handwriting can be acquired in two ways.
- Offline: Images are acquired using an image scanner.
- Online: Acquisition using coordinates in plane and the pressure acquired w.r.t. time.

This project is done by taking data acquired offline, it’s the famous IAM Handwriting dataset.
Concept
Actual traditional way is to establish features like curvature of each type of letter, spacing between letters, etc. and feed them into a strong classifier like SVM to distinguish between the writers. This project is done this task using Deep learning approach to identify such features. We’ll break down images into small patches and feed them to a Convolutional Neural Network and train using a softmax classification loss function. Results obtained are pretty impressive and shows the power of these neural networks.
Data Gathering
The database used contains 1539 pages of scanned text sentences written by 600+ writers. This project uses the top 50 writers with most amount of data. Data is grouped by writers having written a collection of sentences. Example for one of the sentences written by a writer is shown below. I’ve uploaded the curated dataset to Kaggle datasets.

These full pages are shortened and uploaded in the IAM Handwriting dataset in the sentences directory. This data is so elaborate that it has all formats and for all purposes, it also has the file informations in JSON formats. Really fun working with this dataset.
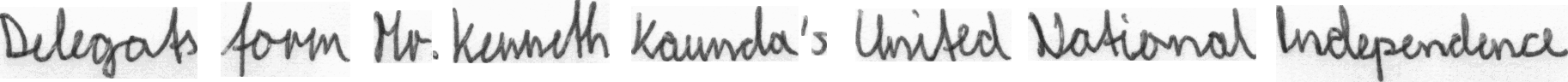

As Neural Networks don’t need much preprocessing of raw data, we keep images unchanged rather we make few patches of the image and pass them.
Preprocessing
For our CNN to understand the writing style, language is not a restriction, so we pass patches of text having image size 113x133 from each sentence. We dont break them w.r.t. sentences or words, but we break them down into smaller image sets.
For serving the purpose, a generator function is implemented to scan through each sentence and generate random patches with same patch size. CNN doesn’t even need to take the full data, so I’ve limited the number of patches to be 30% of the total patches which could’ve been generated from the function. Of course, data-set is shuffled.
Self-designed CNN Model
Keras is a library for deep learning with outstanding results recent days. I’ve used Keras with TensorFlow backend. A standard CNN Model is designed with multiple convolution and maxpool layers, a few dense layers and a final output layer is the softmax activation. ReLU activation was also used between the convolution and dense layers. The resultant model was optimized using Adam Optimizer.
Three blocks of convolution - maxpool layers and a couple of dense layers were sufficent as far as this project is concerned.
Following is the design of the model:
| Layer (type) | Shape | Params |
|---|---|---|
| zero_padding2d_2 (Zero Padding) | (None, 115, 115, 1) |
0 |
| lambda_2 (Lambda) | (None, 56, 56, 1) |
0 |
| conv1 (Conv2D) | (None, 28, 28, 32) |
832 |
| activation_7 (Activation) | (None, 28, 28, 32) |
0 |
| pool1 (MaxPooling2D) | (None, 14, 14, 32) |
0 |
| conv2 (Conv2D) | (None, 14, 14, 64) |
18496 |
| activation_8 (Activation) | (None, 14, 14, 64) |
0 |
| pool2 (MaxPooling2D) | (None, 7, 7, 64) |
0 |
| conv3 (Conv2D) | (None, 7, 7, 128) |
73856 |
| activation_9 (Activation) | (None, 7, 7, 128) |
0 |
| pool3 (MaxPooling2D) | (None, 3, 3, 128) |
0 |
| flatten_2 (Flatten) | (None, 1152) |
0 |
| dropout_4 (Dropout) | (None, 1152) |
0 |
| dense1 (Dense) | (None, 512) |
590336 |
| activation_10 (Activation) | (None, 512) |
0 |
| dropout_5 (Dropout) | (None, 512) |
0 |
| dense2 (Dense) | (None, 256) |
131328 |
| activation_11 (Activation) | (None, 256) |
0 |
| dropout_6 (Dropout) | (None, 256) |
0 |
| output (Dense) | (None, 50) |
12850 |
| activation_12 (Activation) | (None, 50) |
0 |
Usable in Practical Applications
Please fork and use this model, it has high prediciton accuracy. This can be scalable to used in any practical problem you are working on. I’ve uploaded the curated dataset and the model on Kaggle kernels and datasets. Pull requests and merge requests are actively reviewed and updated.